
FAQs
General FAQ
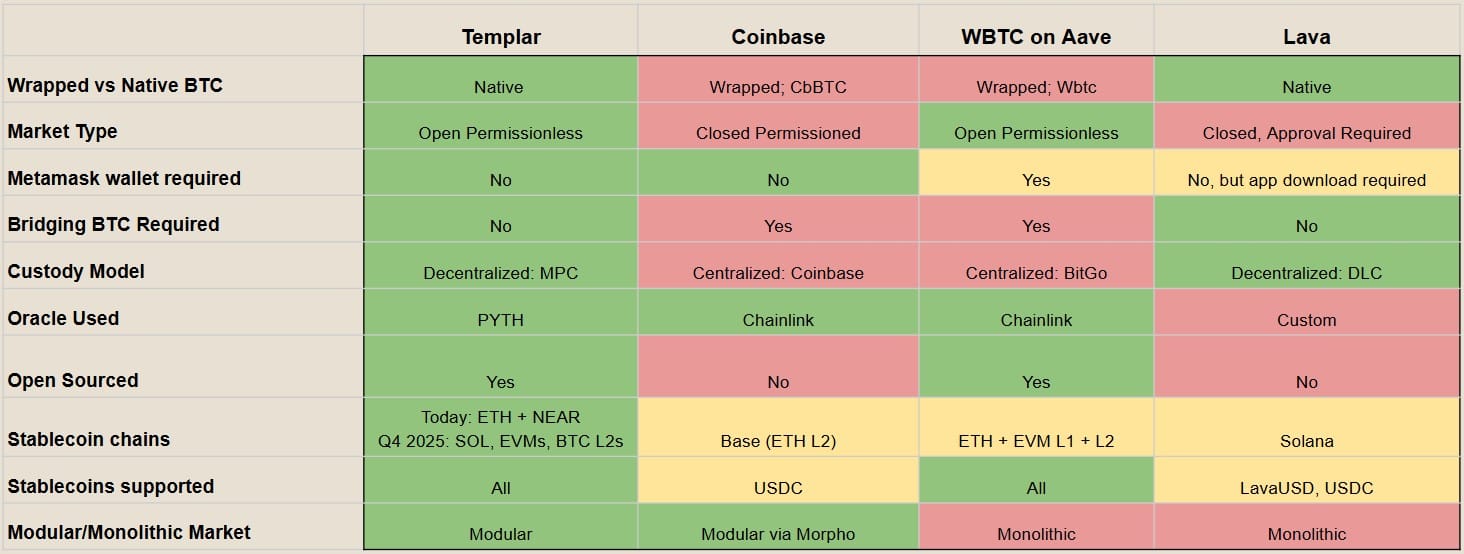
Templar is the first Cypher Lending protocol. It enables users to borrow stablecoins using BTC, or any asset on any chain, without wrapping, bridging, or relying on centralized custodians. It uses a Multi-Party Computation (MPC) network, plus overcollateralization and smart contract liquidations, to stay secure and solvent.
Based on Cypherpunk principles, Cypher Lending enables permissionless borrowing, lending, and deployment of markets for any asset on any chain while:
- Respecting the user’s sovereignty
- Prioritizing privacy and UX
- Open Sourcing all code
- Remaining non-institutional: meaning no Trusted Third Parties or KYC
Templar enables native BTC lending without wrapping, bridging, or centralized intermediaries—unlike bankrupt centralized platforms like BlockFi or Celsius, which lacked transparency and lost users’ funds. The leading decentralized protocols like Aave, Morpho, or Compound rely on wrapped BTC (e.g., WBTC or cbBTC) held by custodians like BitGo or Coinbase. In contrast, Templar uses BTC directly on the Bitcoin network, deposited from your wallet, with full on-chain visibility.
Native BTC Support
Deposit native BTC—no wrapping or bridging. It stays on Bitcoin, secured by a decentralized MPC network (30 nodes). Smart contracts handle borrowing and liquidation permissionlessly, avoiding liquidity fragmentation.
Cross-Chain Lending Without Bridging
Borrow stablecoins on Ethereum using BTC on Bitcoin. Markets are isolated (e.g., BTC → USDC) but coordinate seamlessly via NEAR Chain Signatures—a smart contract–controlled MPC network that signs cross-chain transactions without bridges or wrapped assets.
User deposits native BTC to an MPC Controlled wallet
A NEAR smart contract triggers the MPC network to verify the deposit
Borrowing happens on another chain (e.g., USDC on Ethereum)
No wrapping or bridging - assets stay on their native chain
No. Templar is an open to everyone protocol. There are no plans for mandatory KYC. Optional whitelisting may be supported in the future for custom market types.
Start by opening up app.templarfi.org to access the Templar application front end. For first time users it is recommended to follow the Templar Video Walkthroughs section below.
Templar supports native assets on multiple chains via MPC, Chain Signatures, and NEAR Intents. It avoids bridges and wrappers, letting users borrow/lend directly from BTC, ETH, ADA, DOGE, and other chains using a unified interface.
The new Passkey feature allows users to interact with Templar smart contracts while only having the ability to send and receive your preferred crypto asset.
You can now send a Bitcoin transaction and receive stablecoins on your preferred network—or even directly to an exchange—without needing a smart contract compatible wallet. Templar Protocol will handle all of the smart contract complexities and gas payments for you.
Smart contract compatible wallets (e.g. Metamask, Phantom, Meteor, etc) will always be available for users requiring more control.
Passkeys are the new way to use Templar Protocol in the most seamless way possible. You no longer need to create a NEAR wallet & fund it with NEAR coins to interact with Templar Smart contracts. All gas payments and contract interactions have been abstracted away, only requiring a fingerprint scan or 4 digit code to start borrowing or lending.
NOTE: Passkey functionality has only been tested for Chrome & Brave browsers.
Passkey is the preferred method of interacting with Templar for a couple types of users.
If you don’t have a NEAR wallet & don’t want to create one, this is your best option.
If you’ve never created a crypto wallet you can still interact with Templar by depositing directly from an exchange and withdraw your stablecoins back to an exchange
Passkey is the fastest way to test out Templar Protocol functionality for new users.
NOTE: Passkey functionality has only been tested for Chrome & Brave browsers.
The main costs to interact with Templar are the gas fees for sending a token (e.g., Bitcoin Layer 1 fees, which vary by network conditions), the origination fees to open a loan (when applicable), and the interest paid to borrow against your assets (based on market rates).
No. Templar explicitly avoids rehypothecation. Deposited assets are safely held via MPC custody and never reused for lending or yield farming elsewhere.
No. Templar uses a piecewise interest rate strategy based on usage. Borrowing rates increase as usage rises. A 6% cap can be applied in special LP programs.
Templar cannot freeze user funds. However, some stablecoins may be frozen by the issuer (e.g. Tether, Circle) if the issuer detects criminal activity.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is the technology that lets users send BTC directly into Templar without wrapping or bridging. Templar splits the Bitcoin private key among network parties, each performing a small computation that together forms a standard BTC transaction. In Templar’s MPC system, only one honest participant is needed to prevent dishonest actions—even if all but one collude, that single honest computation blocks fund movement, creating a highly secure system.
Templar uses NEAR’s MPC stack. It's an open-source, cryptographically sound solution based on OT-based threshold signatures (ECDSA) and FROST (EdDSA).
More info can be found here:
The MPC network’s code runs in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), a specialized hardware module that prevents malicious or unauthorized code from running on the nodes. The TEE also ensures node operators’ key shares never leak and protects against long-range attacks.
Looking ahead, Templar plans to enhance security by expanding the MPC network, ultimately incorporating a computation from the user’s computer. This would mean dishonest actions could only occur if the user’s computer is hacked and the MPC network simultaneously goes rogue with the same BTC destination address—an extremely unlikely scenario.
Templar Protocol and the NEAR MPC network do not have centralized custody on user funds. Templar smart contract delegates custody to the NEAR MPC network, which divides custody of users’ funds among the nodes at all times, ensuring no malicious activity occurs as long as one honest participant remains in the network. In the future, Templar plans to include a computational contribution from the user’s computer as part of the MPC network, making malicious behavior nearly impossible. The use of MPC as a solution to the Trusted Third Party Problem was originally proposed by Nick Szabo in 2001.
NEAR Intents provide per-user BTC deposit addresses and verifies BTC transactions via a light client. It acts as the abstraction layer between Bitcoin and NEAR smart contracts, enabling native BTC use as collateral.
Bitcoin FAQ
Depositing BTC to Templar is as simple as it gets. Once the terms of the loan are agreed upon, the protocol provides the user with a QR code or deposit address for a standard Bitcoin Layer 1 transaction. After the transaction is confirmed (2-6 blocks, depending on transaction size), the stablecoins for the loan are released to the user.
You can find a video walkthrough showing the deposit flow at this link.
BTC stays on the Bitcoin network. It’s held by a smart contract-controlled MPC setup, powered by NEAR’s Chain Signatures.The private key is split between 30 MPC nodes (Fireblocks, BitGo, NEAR validators), and no single party can access the funds. Only the smart contract - based on user actions (borrow, withdraw, liquidation) - can trigger a transaction. Funds are never rehypothecated, they only move upon manual loan closure or liquidation.
More info:
Each deposit address is unique and can be verified on any Bitcoin block explorer. You can check BTC addresses and balances on-chain using the public config files, which include:
- BTC collateral address
- NEAR contract that manages BTC collateral (btc.omft.near)
- Pyth price feed ID for BTC
- Vault settings such as liquidation thresholds and address configs
Funds are never re-used or re-hypothecated.
Templar currently accepts only Layer 1 BTC, but we plan to support major BTC LSTs in the future. We will assess engineering timelines and user demand to decide which coins to support first.
Each market in Templar is isolated from the others, so BTC borrowers and lenders are not affected by the collateral or solvency of other markets.
Borrowing FAQ
Borrowing on Templar is extremely simple. To start, a user selects an asset they will be depositing and stablecoin they would like to receive (type and network). The user is then prompted to select how large of a loan they would like to take out. Once the terms of the loan are finalized, a QR code or deposit address is provided to the user as well as a destination address for the stablecoins. When the deposit transaction is finalized (2-6 blocks for BTC depending on size), the stablecoins are released to the address the user provided.
You can find a video walkthrough showing the full borrowing experience at this link.
The amount a user can borrow is a function of many different variables. In particular, the collateral type, dollar amount of collateral provided, the max borrow ratio a market allows, and total amount of stablecoins within the protocol. In general, it is recommended that a user keep 2–3X more collateral in the protocol than loan value to avoid being liquidated during volatile market conditions.
To keep the upside potential of the collateral asset while gaining access to cash and to legally avoid incurring capital gains taxes from selling your assets. Since Templar does not require wrapping or bridging, borrowing does not trigger a taxable event. This is covered more in the use cases portion of the FAQ.
When a user would like to close out their borrow position, they must deposit the original principal taken out on their loan plus any accrued interest/fees. At that time the loan will be closed and the user’s collateral will be released to their desired destination.
Interest costs vary and are market-determined rates. We aim for the average borrow rate to float between 0% to 8%, with discounts for early users, referral codes, and whale deposits. In extreme cases, rates can exceed 10%, but this typically doesn’t last long due to market incentives. Additionally, borrowers earn Templar points that offset some of their interest, sometimes even paying them to borrow.
Borrow positions typically remain open until closed by the user or in the event of a liquidation. However, some loan products have a fixed maximum duration, e.g. 1 year, after which the loan will automatically close if the loan has not already been repaid. Upon auto-closure, the collateral will be used to repay the loan, and any remaining funds will be returned to the user.
Supplying Stablecoins FAQ
For stablecoin lenders, the onboarding process is extremely simple: pick a stablecoin to provide and a market to lend to. Then you send the stablecoins to the provided address and start earning rewards.
You can find a video walkthrough for supplying stablecoins at this link.
Templar currently has markets for USDC and USDT. Templar can add any stablecoin provided there’s pyth oracle support and the stablecoin is on a supported chain. If there’s a stablecoin that meets this criteria, you can create a new market that uses the stablecoin of your choosing.
Templar currently supports sending and receiving stablecoins on NEAR and Ethereum. We will expand to include Solana, Stellar, EVM L1s and L2s, and Bitcoin L2s in the future. You can find the full list of upcoming chain integrations in our Roadmap blog post.
As with most borrowing and lending markets, the primary yield for stablecoin lenders comes from borrowers. This includes several sources: interest rates paid by borrowers, origination fees to open a loan (if applicable), liquidation fees distributed to lenders, and additional incentives Templar may provide like Templar Points & cash incentives.
The yield for lending stablecoins varies depending on market conditions and Templar incentives. In the early days of Templar, yields will be higher due to incentives paid by Templar as USD and as points with total yields being 8-20%+. As time goes on, Templar incentives will play less of a role.
Stablecoins supplied to the protocol are used by borrowers. Overcollateralization requirements ensure there’s always sufficient collateral to protect lenders. During liquidation, lenders receive principal and owed interest, plus a liquidation fee bonus, if applicable.
Funds can be withdrawn any time, but under full usage, a FIFO queue is activated, and when loans are repaid/liquidated or new stables deposited into the market, users will be able to withdraw. Soft lockups apply (token rewards reduced for early withdrawals). High utilization would also mean the interest rate would be quite high, incentivizing new lenders to deposit.
The interest rate borrowers pay lenders follows an adaptive curve based on the percentage of total stablecoins utilized on Templar. For example, it may rise linearly from 2% APR at 0% utilization to 8% APR at 90% utilization. Above 90% utilization, rates increase dramatically to encourage more stablecoins to join the platform and benefit from the high yields. Learn more about this mechanism here.
Liquidation FAQ
Liquidations occur when a borrowed position exceeds its minimum collateral ratio (MCR). Then, the underlying collateral can be purchased at a slight discount by a liquidator in exchange for paying off the loan, ensuring no bad debt for the protocol. Borrowers should avoid this at all costs to prevent losing money and potentially triggering a taxable event by ensuring loans are repaid and sufficient collateral is available to maintain a healthy collateral ratio.
The collateral ratio measures how much collateral a user has compared to their current debt position; it also serves as an indicator of the loan’s health. It’s calculated by dividing the dollar value of the collateral by the amount of debt borrowed against it. For example, if a user has a $100 debt backed by $200 in BTC, the user has a collateral ratio of 200%.
A collateral ratio of 200% to 300% is recommended to avoid liquidation risk. For risk-averse borrowers we recommend 400% or higher to ensure your collateral is highly secure against liquidation, giving you ample time to add more collateral or repay your loan if the market turns unfavorable.
The loan-to-value ratio (LTV), commonly used in finance to measure a loan’s risk, is the inverse of the collateral ratio. For example, a 200% collateral ratio equals a 50% LTV.
Liquidation is triggered at LLTV (83.33% for BTC). Partial liquidations will be enabled for BTC/USDC and WBTC/USDC on Ethereum soon. Liquidators are incentivized stablecoin LPs. Liquidations are executed via AMMs or OTC with solver involvement.
Partial liquidations work by allowing the liquidator to liquidate collateral up until the collateral ratio is considered "healthy" again. For BTC, that's 130% (liquidation at 120%)
Liquidators are also stablecoin LPs, incentivized to act promptly to avoid losses. This dual role aligns economic incentives and ensures pool health.
Yes, liquidation should be avoided at all costs, partly because of the liquidation penalty. This penalty incentivizes liquidators to provide enough stablecoins to close the loan; in return, they purchase your collateral at a slight discount.
The main way to avoid liquidation is to add more collateral, moving your loan’s current borrow percentage to a healthier level. Alternatively, you can repay your loan when it nears the liquidation threshold.
The Minimum Collateral Ratio (MCR) is 120%. Due to the price of Bitcoin falling, a $100 debt position is now backed by $118 worth of BTC collateral, making the loan eligible for liquidation. A liquidator offers $112.10 for the BTC (95% of its value, as priced by an oracle), and the smart contract accepts the bid. The liquidator keeps part of the spread ($118 - $112.10 - slippage) and the stablecoin supplier and the protocol split the remaining amount after the outstanding loan is repaid ($112.10 - $100).
NEAR finality is <1 second, so loan repayment is instant. Releasing collateral from the MPC network takes under 1 minute. Actual withdrawal timing depends on the blockchain — e.g., BTC may take ~10 minutes.
There’s no formal backstop. Liquidators are incentivized via yield. The NEAR Foundation may step in, but this is not guaranteed.
Oracle FAQ
Yes, Pyth is currently the sole oracle, using an EMA + confidence interval approach. Max staleness is 60s. Future plans may consider backup sources if needed.
Templar uses Pyth’s EMA (Exponential Moving Average) prices with confidence intervals. Staleness threshold is 60 seconds. No Chainlink fallback exists on NEAR currently.
Templar uses Pyth oracles with 60s staleness cap and EMA smoothing. Each market config defines the oracle price ID and decimal precision.
Video Walkthroughs
For beginners just starting their Cypher Lending journey with Templar, it is recommended to watch the Introduction Video. You will learn how to get started, open your first loan with BTC, close loans, and supplying stablecoins.
Video Sections:
Bridging assets in and out of crypto protocols can be a massive headache, but not for Templar users. You can watch the Templar Interoperability & Bridging Video to learn how you can easily move assets into Templar from most major blockchains with NEAR Intents. We also walkthrough how you can bridge USDC from NEAR to Ethereum with minimal slippage using Rainbow Bridge.
PS: Users can always withdraw NEAR USDC & USDT directly into a Centralized Exchange to offramp without bridging.
Video Sections:
Ethereum assets are now live on Templar! In this short walkthrough video we showcase how to use a Metamask wallet to open a new loan with Wrapped BTC as collateral & withdraw stablecoins (USDC) back to Ethereum Mainnet.
Stellar assets are now live on Templar! In this short walkthrough video we showcase how to use a Freighter wallet to open a new loan with XLM collateral & withdraw stablecoins (USDC) back to Stellar Network.
Passkey is the new way of interacting with Templar without needing to create a NEAR wallet or use NEAR tokens as gas to interact with our smart contracts. All gas payments and contract interactions have been abstracted away with Passkeys.
In this short video, we showcase how to create a passkey, opening a loan with passkeys, & withdrawing funds back to Ethereum.
NOTE: Passkey functionality has only been tested for Chrome & Brave browsers.
Use Cases of Templar
Unlock BTC liquidity without triggering a taxable event or losing upside potential—especially valuable for long-term Bitcoin holders with significant capital gains.
Borrow stablecoins against BTC without needing a smart contract wallet like MetaMask; users can send a BTC transaction and receive stablecoins directly in their preferred wallet, exchange, or network.
Hedge BTC exposure by using borrowed stablecoins to go short on futures or purchase put options.
Lend stablecoins on Templar to earn yields from interest rates, origination fees, and liquidation spreads.
Increase portfolio leverage through looping, though this is recommended only for experienced DeFi users to avoid potential pitfalls.
Access USD liquidity from BTC without navigating the restrictive KYC/AML processes of centralized institutions.
Earn Templar platform rewards by participating in borrowing or lending; in some cases, this can lead to being paid to borrow, especially in the protocol’s early days.
Deposit borrowed stablecoins into payment platforms that accept them, or convert USD to cover day-to-day expenses.
Protocol Risks and Mitigation FAQ
The risks within Templar arise from the MPC network, general borrow/lend market risks, oracle risk, and smart contract risk. Additionally Templar has plans to create an insurance fund and a roadmap to add additional security features in the future. Each one of these will be explained in more detail below.
Templar splits shards of cryptographic keys among network parties, each contributing computation that forms a standard BTC transaction. With MPC, only one honest participant is needed to prevent dishonest actions; even if all but one party colludes, the single honest computation prevents funds from moving, yielding a 1/N security assumption.
The MPC network’s code runs in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), a specialized hardware module that prevents malicious or unauthorized code from being injected or executed by nodes. The TEE also keeps node operators’ key shards secure and guards against long-range attacks.
Templar plans to enhance security by expanding the MPC network, with the goal of incorporating a computation from the user’s computer. This would limit dishonest actions to cases where the user’s computer is hacked and all of the MPC network members simultaneously go rogue with the same BTC destination address—a highly improbable scenario.
In the future, Templar also plans to support native Bitcoin multisigs for holding collateral where 1 key is held by the user to preserve self custody, 1 by the MPC network, and 1 by either a liquidator or custody provider that supports programmatic access or another MPC network. This allows for fund recovery in the event of MPC network down time.
Borrowing and lending platforms face the risk of bad debt leading to insolvency, a common issue with centralized institutions like BlockFi and Celsius in the crypto industry. In contrast, smart contract-enabled platforms like Aave and Templar mitigate this through overcollateralization and automated liquidations. Each Templar market has a minimum collateral ratio (MCR). When a loan is below the MCR, liquidators can liquidate the position by supplying stablecoins matching the user’s original principal, interest, and fees. In return, liquidators purchase the collateral at a discount, creating free-market-driven incentives to prevent bad debt in the protocol.
The MPC network currently has 30 nodes. These include top custody providers like Fireblocks and BitGo, as well as NEAR validators. The private key for each market is sharded among them using secure multiparty computation.
MPC nodes are run by top custody providers (e.g., Fireblocks, BitGo) and leading NEAR validators. The NEAR Foundation is actively working on further decentralizing the network. More info on future of MPC decentralization
A 2/3 multisig recovery model (user + MPC + third party) is planned for Q1 2026 to improve recoverability and decentralization. This allows users to recover funds even if MPC is temporarily offline. TEEs are used to protect private key shards to avoid downtime.
To maintain overcollateralization, Templar requires real-time collateral valuation. We leverage the industry-leading Pyth oracle, which averages BTC prices across major centralized exchanges and uses a smoothed moving average to ensure accuracy and prevent oracle manipulation. Additionally, each lending market is isolated; if bad debt or market contagion occurs, it remains confined to that market. By contrast, a pool-based model lets contagion spread across markets, assets, and users.
Smart contract risks can be reduced through audits. Templar is engaging three auditing firms with expertise in Bitcoin integration, Solidity, and the NEAR tech stack to rigorously test borrowing, lending, and liquidation functions under various market conditions. Templar audits can be found at the following GitHub link.
Auditors: Thesis Defense, Guvenkaya, Certora. Reports:
Certora audit is in remediation. Critical issues have been fixed and merged.
Templar uses formal verification audit(by Certora), open-source audits, no admin keys, fuzzing, peer reviews, and TEE-based MPC nodes. The third audit is finishing, and formal audit by Certora is ongoing.
Templar contracts are immutable, with no proxy pattern or admin keys. Changes are made by deploying new contracts (versioning), similar to Uniswap or Bitcoin Core. This guarantees no centralized control over deployed markets.
Each market is deployed as its own immutable contract. In case of critical bugs, a new market is deployed, and users are contacted directly to migrate liquidity manually.
No, the Templar team cannot steal users’ funds. We lack admin or multisig access to the smart contracts or their associated funds, ensuring that control remains fully decentralized and secure.
No insurance fund is live yet. A dedicated, on-chain and legally separate insurance fund is planned ~6 months post-launch.
Templar Points and Incentives FAQ
Templar Points are our way of tracking and acknowledging Templar’s earliest supporters before we launch a token to incentivize borrowers and lenders. They accumulate for individual addresses, with rewards distributed later. The number of points awarded decreases over time, ensuring early users who take the greatest risks and bootstrap protocol liquidity are compensated most.
Templar incentivizes borrowing and lending with USD-based rewards to boost protocol liquidity in the early days. These include lower borrowing rates and higher lending yields.
Privacy FAQ
Templar does not collect or store personal information from any users. This is one of the key principles of Cypher Lending.
Templar prioritizes user privacy and plans to enhance it over time. To prevent predatory liquidation hunting, we’ll implement differential privacy. Additionally, zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-proofs) will be used to maintain on-chain privacy, keeping loan information confidential while still verifiable. The Templar privacy roadmap can be found at this link.
Invite Codes and Ref Links FAQ
Templar invite codes and referral links are used to gain access to markets with favorable interest rates and to track how much liquidity individual users bring in, rewarding them for helping grow the protocol.
Advanced FAQ
Yes, users can deploy their own markets on Templar, which is designed to be fully customizable. Our goal is to let the market determine the optimal settings for key variables, allowing the most effective markets to attract the greatest liquidity. The full list of configurable market parameters are available here.
Brand FAQ
The Templar logo and wordmark are available in black, white, and ivory at this link.
The Templar team reserves the right to request removal if the content misrepresents the brand.
No: all Templar brand elements are reserved for our products. The Templar team may request removal of content we don’t endorse.
You can create images and content using Templar brand elements; however, the Templar team reserves the right to request removal of any content.
Future Additions FAQ
Initially, Templar doesn’t natively support vault creation. Over time, we plan to introduce this feature, enabling advanced users to design and manage strategies that optimize risk and return by leveraging multiple markets. Other users will be able to invest capital in these vaults, paying a small fee to the vault curator.
Templar’s roadmap focuses on enhancing its trust-minimized, privacy-first, chain agnostic lending platform with the following features:
Privacy Enhancements: Private lending via ZCash & its shielded asset technology, wallet-less usage, differential privacy for liquidation obfuscation, onchain cash markets, and zero-knowledge smart contracts.
Product Features: Flexible market parameters (rate curves, loan durations, fees), curated DeFi vaults, chain-abstracted markets, sponsored gas transactions, partial liquidations, fixed interest rate loans, yield accrual on collateral, and a JS SDK for developer integrations.
Ecosystem Integrations: Adapters for external lending protocols, yield and positional token integration.
For full details, see the Templar Roadmap.